Table of contents
Potentiometer
A potentiometer is a sensitive electronic device used to measure cell, find internal resistance of cell and to compare the e.m.f of two cells.
Principle
When a constant current is passed through a wire of uniform area of cross- section the potential drop across any position of wire is directly proportional to the length of that portion.
i.e., V=IR = I× PA
V∞ 1 for constant 'A' and 'I'
This is the working principle of potentiometer
Here,
V=Potential difference
I = Current
R=Resistance of wire
A = Cross sectional area of wire
p = Resistivity
Read more = state Brewster law in physic ?
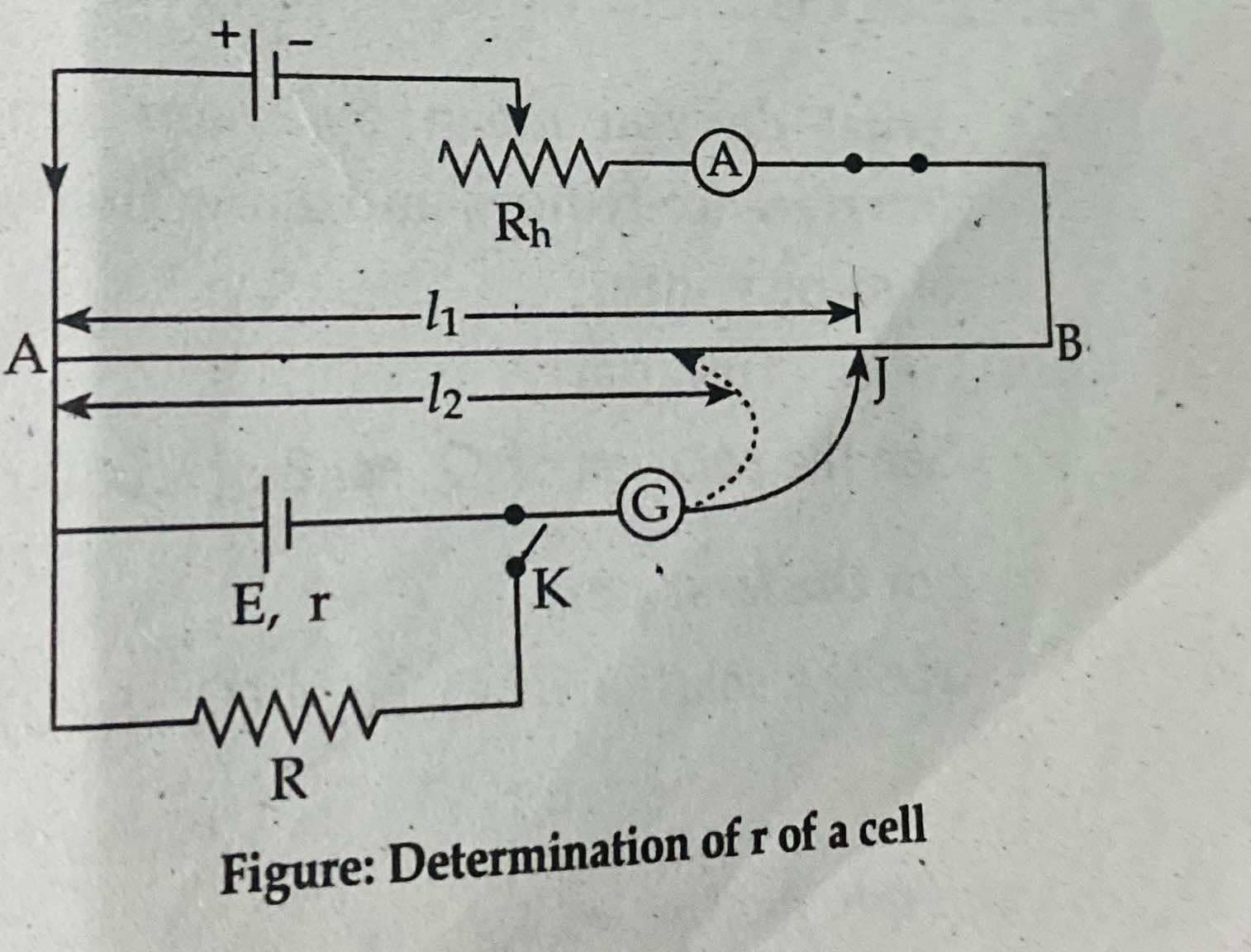
Determination of the internal resistance 'r' of cell by using potentiometer
An external resistance 'R' is connected across parallel to the AP cell. When the key 'k' is open i.e., open circuit; there is no current flowing through 'R' and P.D is equal to 'E' of cell. In this condition, the balancing length is l1. If 'L' is the total length of wire. Then,
E=l1/L *VO
where, Vo is the potential difference across whole length.
When key 'K' is closed, i.e., circuit is closed so that current flows through resistance 'R' as well the jokey gives new balancing length l2. The p.d. "'V' in this case is equal to potential drop across 'R'. So,
V=L2/L *v0
Dividing equation (1) by (2), we get,

Hence, by knowing the value of L1, l2 and R, the equation (4) gives the internal resistance of the cell by using potentiometer.
Comments ( 5 )